Navigating currency markets can be a thrilling yet complex endeavor. Understanding the difference between speculation and hedging is key for anyone involved. While speculation focuses on profit through market predictions, hedging aims to protect against financial risks. This guide delves into these strategies, offering insights into their unique mechanisms and applications. Understanding the differences between speculation and hedging is vital for effective currency trading. Immediate Wealth connects traders with experts who can help clarify these concepts and enhance trading strategies.
Objectives and Motivations Behind Speculation and Hedging
Speculation and hedging serve distinct purposes in the currency markets. Speculation is primarily driven by the desire to make profits from market fluctuations. Speculators analyze trends, news, and economic indicators to forecast future currency movements.
They aim to buy low and sell high, often employing leverage to maximize gains. The allure of high returns in a short period is a significant motivator, but it also comes with considerable risk.
Hedging, on the other hand, focuses on risk management. Businesses and investors use hedging to protect against unfavorable currency movements that could impact their operations or investments.
The primary goal is to ensure financial stability and predictability. For instance, a company with international operations might hedge to lock in exchange rates, safeguarding their profits from adverse currency fluctuations. Hedging strategies are akin to buying insurance; they come at a cost but provide peace of mind by minimizing potential financial setbacks.
Mechanisms and Strategies in Speculation
Speculation in currency markets involves various techniques aimed at capitalizing on short-term price movements. Day trading is a popular method where traders buy and sell currencies within a single day to avoid overnight risk.
Scalping takes this a step further, with traders making numerous small trades throughout the day, holding positions for mere minutes or seconds to profit from tiny price changes.
Leverage is a key tool for speculators. By using borrowed funds, traders can control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital, amplifying both potential gains and losses. For instance, with 10:1 leverage, a trader can control $10,000 worth of currency with just $1,000. This high-risk, high-reward approach requires strict risk management practices. Stop-loss orders are essential, automatically closing trades if the market moves against the trader to limit losses.
Speculators also stay attuned to economic news and events, such as central bank announcements, geopolitical developments, and economic data releases. These events can cause significant market volatility, presenting opportunities for profit.
The key to successful speculation lies in quick decision-making and the ability to anticipate market reactions to various stimuli. While the potential for profit is high, so is the risk, making speculation a strategy best suited for experienced and risk-tolerant traders.
Mechanisms and Strategies in Hedging
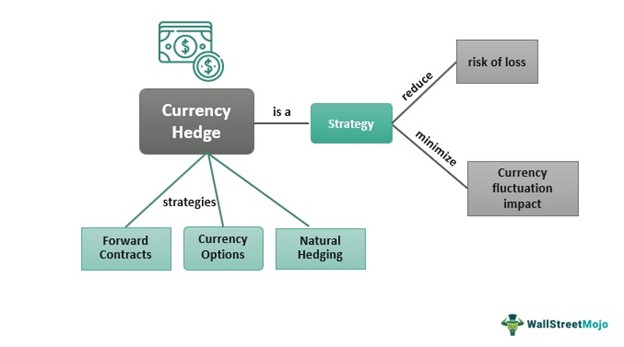
Hedging strategies in the currency markets are designed to manage long-term risks and provide financial stability. One common approach is using futures contracts, which allow businesses to lock in an exchange rate for a future date. This ensures that future financial transactions are not adversely affected by currency fluctuations.
Options contracts are another valuable hedging tool. Unlike futures, options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to exchange currencies at a predetermined rate. This flexibility is particularly useful when there’s uncertainty about future market movements. If the market moves favorably, the option can be left to expire, but if it moves unfavorably, the option provides a safety net.
Currency swaps are also widely used in hedging. These involve exchanging principal and interest payments in different currencies, which is beneficial for long-term projects. For instance, a company operating in multiple countries might enter a swap agreement to manage the risk of currency fluctuations affecting their operational costs and revenues.
Forward contracts, customizable agreements to exchange currencies at a future date and rate, are favored for their flexibility. They allow businesses to tailor hedging strategies to specific needs and timeframes.
By employing these instruments, companies can achieve greater financial predictability, ensuring that their international operations are not disrupted by unforeseen currency movements. Hedging is thus a vital strategy for mitigating risk and securing long-term financial health.
Financial Instruments Utilized in Speculation vs. Hedging
Speculation and hedging in the currency markets rely on different financial instruments, each serving unique purposes. For speculators, derivatives like futures and options are primary tools. Futures contracts enable traders to bet on the future price movements of currencies, providing opportunities to profit from anticipated changes.
By agreeing to buy or sell at a specific price on a future date, speculators can leverage their market predictions. Options contracts offer another avenue, granting the right but not the obligation to trade currencies at a set rate, allowing traders to benefit from favorable movements while limiting potential losses.
Hedging utilizes a different set of instruments aimed at risk management. Currency swaps are a key tool, involving the exchange of principal and interest payments in different currencies.
This is particularly useful for businesses engaged in long-term international projects, as it helps manage the risk of currency fluctuations over extended periods.
Forward contracts, customized agreements to exchange currencies at a future date, provide flexibility and are tailored to specific needs, making them ideal for businesses seeking to lock in rates and avoid adverse market movements.
Conclusion
Mastering speculation and hedging in currency markets can significantly enhance financial outcomes. Speculation seeks quick profits, while hedging ensures stability. Both strategies, when used wisely, offer valuable tools for managing currency exposure. Always consult financial experts to tailor these approaches to your specific needs and goals.